
Modalities
Modalities
At Agape, various modalities are used to enhance your therapy treatment and recovery.
This list includes many of our modalities. Our goal is more of a hands on approach, but modalities are tools that can aid in the process.
- Electrical stimulation
- Interferential Current (IFC)
- Ultrasound
- Iontophoresis
- Anodyne
- Traction
- Hot packs
- Cold packs
- FAT tool
- Neuromuscular stimulation
- Biofeedback
- MR cube
- Aquatic therapy
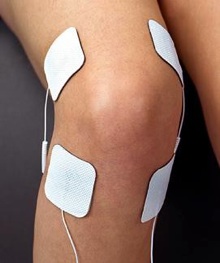 |
Electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation uses an electrical current to cause a single muscle or a group of muscles to contract. By placing electrodes on the skin in various locations the Physical Therapist can recruit the appropriate muscle fibers. Contracting the muscle via electrical stimulation helps strengthen the affected muscle. The Physical Therapist can change the current setting to allow for a forceful or gentle muscle contraction. Alone with increasing muscle strength, the contraction of the muscle also promotes blood supply to the area to assist in healing.
|
 |
Interferential current (IFC)
Interferential current therapy is a treatment to aid the relief of pain and the promotion of soft tissue healing. Tiny electrical impulses are induced into the tissues in the area of the pain. Where these waves intersect below the surface of the skin, the low frequency stimulation induces the body to secrete endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain killers. Most patients find interferential therapy to be very beneficial and describe the treatment as being relaxing and having a ‘pins and needles’ sensation. Ligament sprains, muscle strains, and muscle spasms often respond well to interferential current therapy.
|
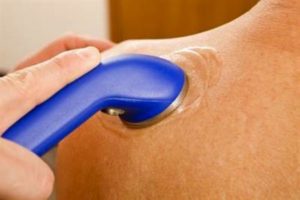 |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound therapy uses high energy sound waves (those above the range we can hear) to help ease painful joints and muscles. Ultrasound treatment is done by a Physical Therapist or Occupational Therapist who guides the waves into the tissue from the head of an ultrasound machine |
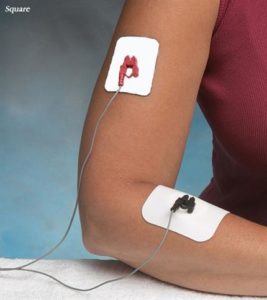 |
Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is a treatment for inflamed joints and muscles and is regaining recognition as as substitute to injections and other treatments. The practice was first developed in the mid 1700s and involved the introduction to various medications (in the form of ions) through the skin by means of electricity. Using a low volt direct electrical current, an ion acting as an anti-inflammatory or pain relieving medicine, penetrates the skin into the painful area and cures the troubled area.
|
 |
Anodyne (infrared) therapy
Anodyne is a treatment that uses energy, which dramatically increases circulation in the area to which it is applied. Light emitting diodes are fitted into flexible pads that can be applied directly to the skin on any part of the body. The light energy helps increase blood flow by delivering healing cells and nutrients to the injured site.
|
 |
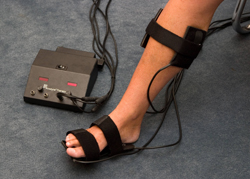
Traction
Traction is defined as the act of pulling or a state of being pulled. The purpose of this treatment is to alleviate pain by relieving pressure and improve mobility of either nerve structures, joints of the spine, and/or muscles. Some of its many uses include the following: improve joint mobility of spinal facet joints, relieve nerve impingement due to disc herniation or bony compromise,alleviate muscle spasms cause by injury, and to decompress arthritic joints caused by degenerative disc disease or osteoarthritis. Our therapists use both cotrel and manual traction.
|
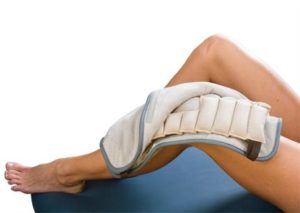 |
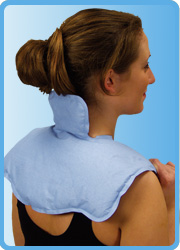
Heat packs
Heat therapy is the use of heat in the form of hot compresses, heat lamps, or heating pads to cause blood vessels to dilate and increase blood flow to the injury site. Increased blood flow aids in the healing process
|
 |
Cold packs
Using ice to treat injuries is one of the oldest methods of pain control. Proven to be safe and effective at reducing swelling, relieving pain and decreasing muscle spasms, ice therapy is an easy self-care technique that anyone can administer.
|
 |
FAT tool
To learn more about the FAT tool, please click here.
|
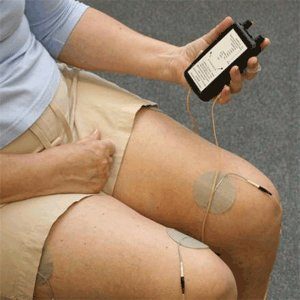 |
Neuromuscular stimulation
Neuromuscular stimulation (NMES), also known as therapeutic (or threshold) electrical stimulation (TES), is a form of electrical stimulation that attempts to strengthen muscles weakened by disuse. TES uses sub-contraction stimulus to promote muscle growth. Normally in an individual with disuse atrophy, contracting muscles use the strongest fibers available, so weakened muscles do not respond and deteriorate further. NMES is used at night during sleep, and is purported to increase blood flow to the muscles in which fibers are atrophied. NMES can also be used in the outpatient setting as an adjunct therapy to treat muscle atrophy.
|
 |
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a complementary technique in which you learn to sense different actions of your body, such as heart rate and muscle tension. With biofeedback, you’re connected to electrical sensors that help you measure and receive information (feedback) about your body (bio). The biofeedback sensors help you learn to make subtle changes in your body, like relaxing certain muscles, to achieve the results you want (ie. reducing pain).
|
 |
MR Cube
The MR cube is a training and rehab tool designed to improve development of the neuromuscular system. It allows for the improvement in control, coordination, reaction time, power and strength while providing a fun, motivating workout through video game interaction. It is currently being used by a majority of professional sports teams, especially in the NFL, due to its faster recovery time for athletes from both post-surgical and acute injuries. |

